MỤC LỤC

When evaluating debt ratio values, consider the context and industry standards. Typical benchmark ranges often vary but generally, a debt ratio below 0.5 indicates a balanced leverage position. Ratios exceeding 0.5 may warrant further analysis to determine if high leverage reflects aggressive growth strategies or excessive financial risk.
- Understanding the different types of debt ratios is essential for managing debt effectively.
- The significance and interpretation of the debt ratio can fluctuate noticeably under various economic conditions.
- By creating a budget, paying down high-interest debt, and avoiding new debt, you can set yourself up for financial success in the long run.
- For example, a company may have a high debt-to-equity ratio but a high interest coverage ratio, which may indicate that it is using debt effectively to generate earnings.
- In the business world, debt is a common tool used to finance operations, growth, and expansion.
Debt Ratio Trends: What They Reveal About Long-Term Financial Stability
If a company has a high level of debt and interest rates rise, the cost of debt might become unsustainable, putting the company at risk despite an acceptably low debt ratio. It’s important investors consider not just the current debt ratio, but how changes in interest rates could affect the company’s financial stability. The value of total assets can fluctuate due to market conditions, accounting practices, or asset write-downs, potentially distorting the https://pulom-cap.com/blockchain-in-banking-benefits-for-the-industry/ debt ratio. A very low debt ratio might indicate under-utilization of financial leverage, where the company needs to take advantage of debt to fuel growth. By understanding the factors that influence the debt ratio, small business owners can make informed decisions about their debt management and financial planning.
The Debt Ratio Formula: How to Calculate Debt Ratio
AI and machine learning algorithms can quickly analyze vast amounts of financial data to identify trends and potential risks. This can help businesses make more informed decisions about their financing options. However, it’s a debt ratio of 0.5 indicates: important to note that these tools are only as good as the data they’re based on. As such, it’s crucial to ensure the accuracy and completeness of financial data before feeding it into these algorithms.
Company’s Stage of Growth
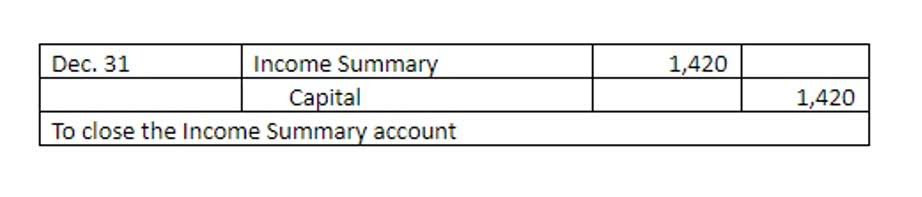
In the realm of finance, a high debt ratio can be a precarious position for any company, signaling potential distress and the need for strategic maneuvers to ensure solvency. This ratio, which compares a company’s total debt to its total assets, serves as a critical barometer for investors, creditors, and the company’s management to gauge financial health. A high debt ratio suggests that a company may be over-leveraged, relying heavily on borrowed funds to finance its operations and growth.

What is good current ratio?
A debt ratio of 0.5 means that 50% of the company’s assets are financed by debt. A debt ratio of 1 would indicate that the company has equal amounts of debt and assets, while a ratio greater than 1 would indicate that the company has more debt than assets. Moreover, the debt ratio doesn’t provide a complete picture of a company’s financial health.
For example, capital-intensive industries like utilities or manufacturing often have higher D/E ratios due to the need for substantial infrastructure investments. Comparing a company’s D/E ratio to industry peers can provide valuable context. It’s essential to conduct industry-specific analysis to determine what level of leverage is considered healthy within a particular sector. The debt to asset ratio is a valuable metric for assessing a company’s financial leverage and stability.

For example, a debt to equity ratio of 1.5 means a company uses $1.50 in debt for every $1 of equity i.e. debt level is 150% of equity. A ratio of 1 means that investors and creditors equally contribute to the assets of the business. Let us, for instance, determine the debt-to-asset ratio of Bajaj Auto Limited, a prominent automotive manufacturing organization situated in India. The total liabilities of Bajaj Auto Limited as of 31 March 2024 were Rs 13,937 crore, as indicated in their balance sheet. Therefore, the debt ratio is very significant in measuring the financial leverage of the company. The ratio tells the investors how leveraged the firm is because a company that has a higher level of liabilities compared to its assets, has more financial leverage and vice versa.
- Startups may have higher debt ratios due to initial capital needs, while established companies might operate with lower ratios.
- To calculate the debt ratio, begin by identifying the total liabilities from the company’s balance sheet, which include both current and long-term obligations.
- Past performance does not guarantee future results, and investment values may rise or fall.
- The maximum permissible debt ratio for some companies is 1.5-2 or less, while large companies with a debt ratio score greater than 2 are considered acceptable.
Taking on debt may be your best option when you don’t have enough equity to operate. The accounting debt-to-equity ratio can help you determine how much is too much and draws the line between good and bad debt ratios. A low debt to assets ratio, typically around 0.5 or lower, indicates a healthy financial base and reduced financial risk. However, a debt ratio greater than 1 indicates high future financial risk. Investors use the debt-to-asset ratio to assess financial risk before investing in a company.

What Is a Good Debt to Asset Ratio for Financial Stability
This low debt ratio reflects Apple’s how is sales tax calculated conservative financial management strategy, which prioritizes cash reserves and conservative debt levels. By keeping its debt levels low, Apple is able to maintain its financial flexibility and weather economic downturns more effectively. Interpreting the D/E ratio should be seen in the context of a company’s growth strategy and risk tolerance.
How to Spend Your PPP Funds (Updated for
Some companies purposefully maintain a higher D/E ratio to leverage financial leverage for rapid expansion or investment in new projects. On the other hand, businesses in more stable industries may choose to maintain a lower D/E ratio to minimize financial risk. It’s a fine balancing act between maximizing growth opportunities and safeguarding against potential financial distress. The interest coverage ratio measures a company’s ability to pay its interest expenses on its outstanding debt.


